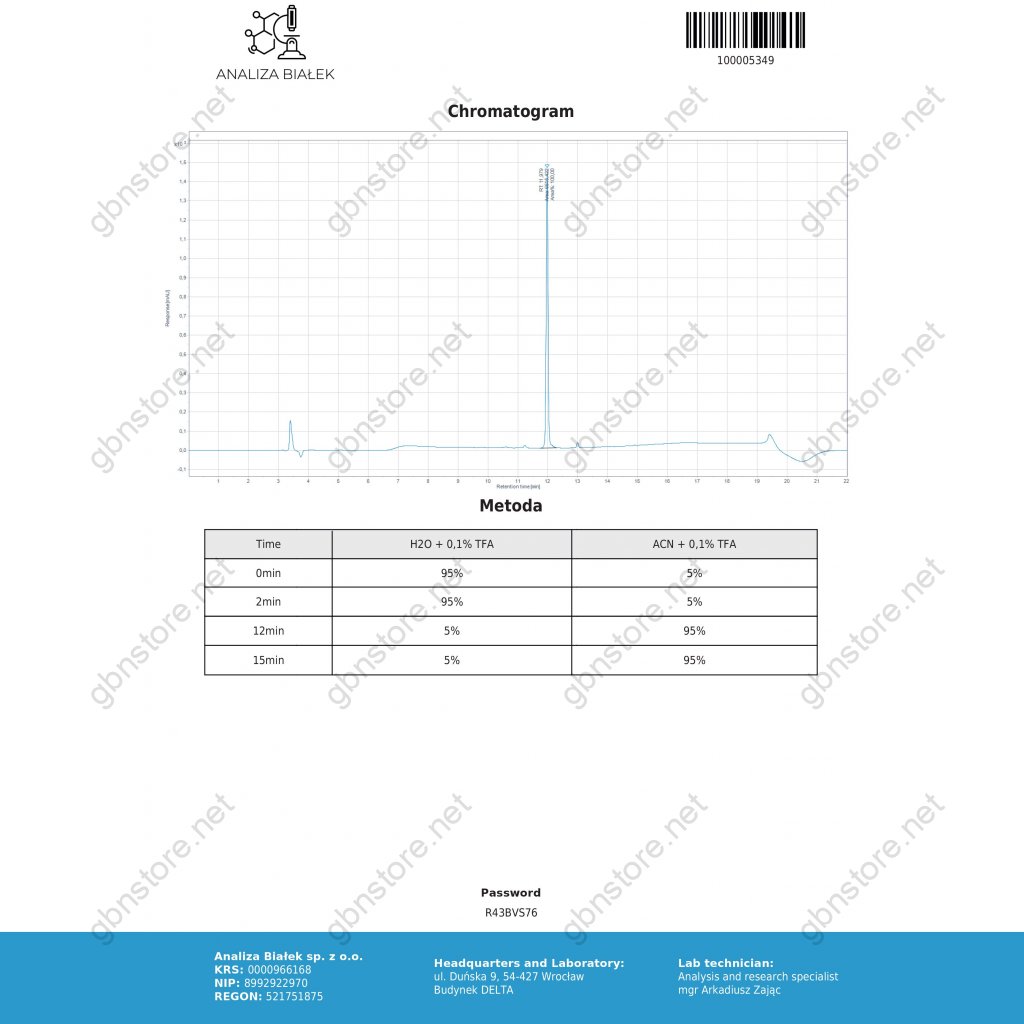




MANUFACTURER: Dragon Pharma, Europe
ACTIVE INGREDIENT: Tirzepatide
STRENGTH: 5 mg
AMOUNT: vial
Introduction
Tirzepatide, a revolutionary drug candidate under the spotlight in the medical field, holds promise as a dual GIP (glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide) and GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) receptor agonist. Developed by the pharmaceutical company Lilly, it is currently in the late stages of clinical trials for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and obesity. This article aims to elucidate the molecular mechanism of action, therapeutic potential, and the clinical significance of tirzepatide.
Molecular Mechanism of Action
Tirzepatide is a once-weekly injectable medication that works by mimicking the actions of two incretin hormones—GIP and GLP-1. Incretin hormones are naturally occurring peptides that play a critical role in regulating glucose homeostasis. Upon food intake, they stimulate insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells while simultaneously suppressing glucagon release from alpha cells and slowing gastric emptying, which reduces postprandial glucose excursions. Additionally, they promote satiety and reduce food intake through their action on the central nervous system. By acting on both GIP and GLP-1 receptors, tirzepatide enhances the body's ability to manage blood sugar levels effectively and may offer a more robust treatment option than existing single-receptor agonists.
The dual agonism of tirzepatide is a novel approach in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. The GIP receptor agonist component is known to increase insulin sensitivity and beta-cell function, whereas the GLP-1 receptor agonist component is recognized for its glucose-lowering effects by stimulating insulin secretion and suppressing glucagon release. The synergistic action of these two hormones is believed to contribute to the overall efficacy of tirzepatide. Moreover, tirzepatide's prolonged half-life allows for once-weekly dosing, offering convenience to patients and potentially improving adherence to treatment regimens.
Therapeutic Potential
The therapeutic potential of tirzepatide is substantial, given the growing prevalence of type 2 diabetes and obesity. As a potent incretin mimetic, it has the capability to address multiple facets of these metabolic conditions. In clinical trials, tirzepatide has demonstrated significant improvements in HbA1c levels, a key indicator of long-term blood sugar control, and substantial weight loss in patients with type 2 diabetes. The medication appears to be well-tolerated, with adverse effects such as nausea and diarrhea, which are common with GLP-1 receptor agonists, being generally mild to moderate.
The SURMOUNT-1 trial, a phase 3 randomized controlled trial, compared tirzepatide to the widely used GLP-1 receptor agonist semaglutide and to insulin glargine, a long-acting insulin. The results were astonishing, with tirzepatide showing superiority in reducing HbA1c levels and body weight compared to both treatments. This suggests that tirzepatide could become a first-line treatment option for patients with type 2 diabetes who are not adequately controlled with existing medications. Furthermore, tirzepatide's dual mechanism of action may also offer benefits in reducing cardiovascular risks associated with diabetes, an area of significant concern in this patient population.
Clinical Significance
The introduction of tirzepatide could revolutionize the treatment landscape for type 2 diabetes and obesity. If approved, it would provide a new treatment choice for patients who have not responded optimally to existing therapies or for those who are intolerant of the side effects associated with current medications. The dual targeting of GIP and GLP-1 receptors represents a new paradigm in the treatment of these conditions, potentially offering superior glycemic control and weight management.
Moreover, the convenience of once-weekly dosing may appeal to patients who struggle with the daily injections required by some current treatments. This could lead to better adherence and, consequently, improved health outcomes. The clinical significance of tirzepatide also extends to its potential cost-effectiveness, as it may reduce the need for multiple medications and hospitalizations due to poorly controlled diabetes.
Conclusion
Tirzepatide represents a significant advancement in the treatment of type 2 diabetes and obesity. Its unique dual mechanism of action and favorable clinical trial results suggest that it could become a cornerstone of diabetes management. Further research is necessary to fully understand its long-term efficacy and safety profile, but the promise is undeniable. As we await the final trial results and regulatory decisions, the scientific community eagerly anticipates the potential impact of this innovative therapy on the lives of millions of patients worldwide. You can read more about Tirzepatide on our online knowledge base.
Please log in to write Tirze-pep review.